Date:2021-10-31 | Visitcount:425
In Oct. 2021, Prof. Haiyan Cen's group published a research paper on Remote Sensing of Environment (JCR,Q1), which is one of the top journalsin the field of remote sensing, with 5-year impact factor of 11.057, entitled “PROSDM:Applicability of PROSPECT model coupled with spectral derivatives andsimilarity metrics to retrieve leaf biochemical traits from bidirectionalreflectance”.
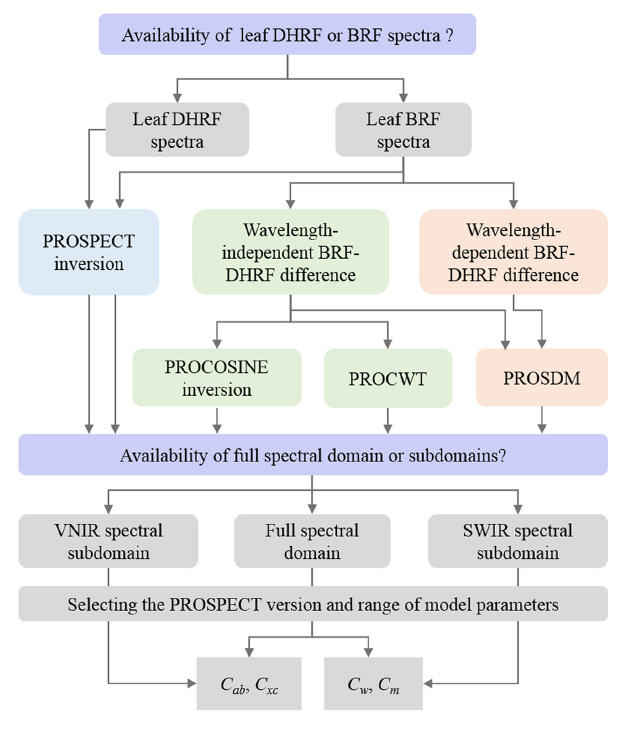
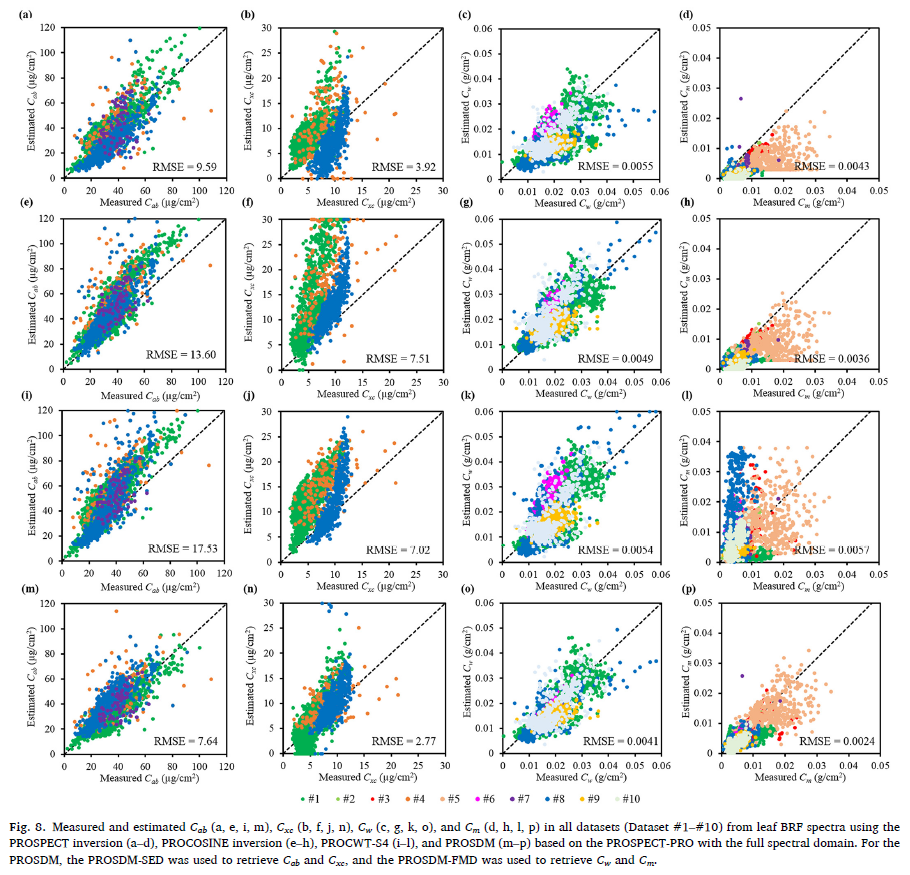
The PROSPECT model, one of the most popular leaf radiative transfermodels, has long been used for retrieving leaf biochemical traits from leafdirectional-hemispherical reflectance factor (DHRF) spectra, while remains underexploredfor applications to the leaf bidirectional reflectance factor (BRF) spectra toretrieve leaf biochemical traits. Existence of leaf surface reflectance andanisotropic property could be the main issues that constrain the applicabilityof the PROSPECT inversion to assess leaf biochemical traits from leaf BRFspectra. This study presents an inversion method by integrating the PROSPECTmodel with spectral derivatives and similarity metrics (SDM), called PROSDM, toremove the difference between leaf BRF and DHRF spectra and retrieve leaf biochemicaltraits from leaf BRF spectra. Leaf BRF spectra and the corresponding contentsof chlorophyll (Cab), carotenoid (Cxc), water (Cw), and dry matter (Cm) wereobtained from ten datasets across a wide variety of plant species with variedgrowth stages, nutrition status, and planting regions. The datasets showed thatthe significant difference existed between leaf BRF and DHRF spectra, whichvaried with spectral wavelengths and plant species, and affected the accuraciesof retrieving Cab, Cxc, Cw, and Cm. To eliminate the difference between leafBRF and DHRF spectra independent on wavelengths, spectral derivatives wereapplied. When the difference between BRF and DHRF spectra varied withwavelengths, spectral derivatives only removed part of the difference, and implementationof the Manhattan distance compensated the limitation of the spectralderivatives to further reduce the difference. As a result, the PROSDMoutperformed the PROSPECT and PROCOSINE inversions as well as PROCWT toretrieve Cab, Cxc, Cw, and Cm from leaf BRF spectra with the root mean squareerrors (RMSEs) of 7.64 μg/cm2, 2.77 μg/cm2, 0.0041 g/cm2,and 0.0024 g/cm2, respectively. Significant improvements in the retrievalsof Cab, Cxc, Cw, and Cm were obtained with the RMSEs reduced by 20.33%, 29.34%,25.45%, and 44.19% compared to the PROSPECT inversion, respectively. It wasfurther found that the model inversions were affected by the spectralsaturation, PROSPECT versions, spectral subdomains, and the range of modelparameters. The retrieval results by different inversion methods may beimproved with the suitable spectral subdomains and range of model parameters.Importantly, the proposed PROSDM showed the great potential to alleviate these negativeeffects on the retrievals of Cab, Cxc, Cw, and Cm. The performance assessmentof PROSDM demonstrates a promising potential for its applications in remotesensing aiming at retrievals of leaf biochemical traits from leaf BRF spectra.