
Date:2021-11-23 | Visitcount:439
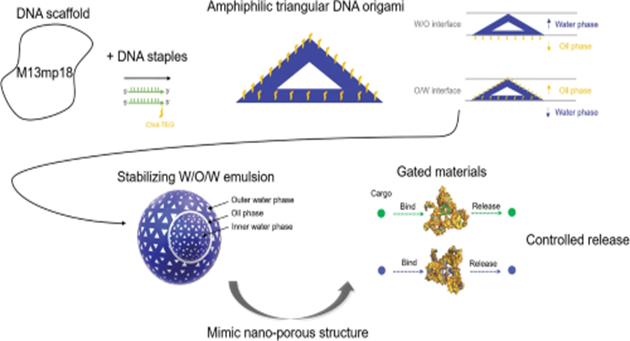
Recently, the team of Prof. Xingyu Lin and Prof. Zisheng Luopublished a cover paper in the international authoritative journal Small(IF=13.281) entitled “Amphiphilic and Biocompatible DNA Origami-based EmulsionFormation and Nanopore Release for anti-melanogenesis Therapy.” In this paper,amphiphilic triangular DNA origami was successfully designed to attach to theoil-water interface to stabilize the water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsionseparately, and controlled release of phenolic compounds arbutin and coumaricacid was realized based on the center hole of DNA origami.
The first author of this paper is Huang Hao, a doctoralcandidate majoring in food science of our college, and the correspondingauthors are Professor Luo Zisheng and Professor Lin Xingyu of our college.Zhejiang University is the first signed unit.

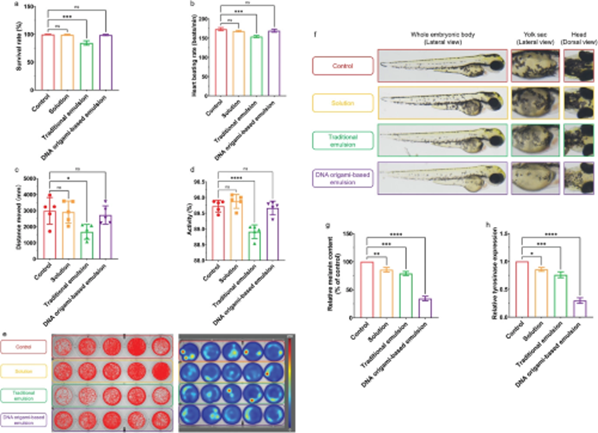
Here, a strategy for fabricating anamphiphilic triangular DNA origami with a central nanopore that integratesphase-stabilizing, porous-gated, and affinity-delivering effects is presented.By introducing the DNA origami as a single-component surfactant, thewater-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsion is effectively stabilized with decreasedinterfacial tension. Microscopic observation validates the attachment of theDNA origami onto the water-in-oil and oil-in-water interfaces. Furthermore,fluorescence studies and molecular docking simulations indicate the bindinginteractions of DNA origami with arbutin and coumaric acid at docking siteswithin central nanopores. These central nanopores are functionalized asmolecular gates and affinity-based scaffold for the zero-order release ofarbutin and coumaric acid at a constant rate regardless of concentrationgradient throughout the whole releasing period. In vivo zebrafish resultsillustrate the advantages of this zero-order release for anti-melanogenesistherapy over direct exposure or Fickian diffusion. The DNA origami-based W/O/Wemulsion presents anti-melanogenic effects against UV-B exposure withoutcardiotoxicity or motor toxicity. These results demonstrate that this non-toxicamphiphilic triangular DNA origami is capable of solely stabilizing the W/O/Wemulsion as well as serving as nanopore gates and affinity-based scaffold forconstant release.
Since the materials and solvents usedin this study were non-toxic, THE DNA origami stabilized W/O/W emulsion had thepotential to be applied to food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic fields to achieveexcellent whitening effects and safety assurance.
This study was supported by the National Key RESEARCH andDevelopment Program, The Ten Thousand People Program of Zhejiang Province, andthe Hangzhou Agricultural Development Research Program.
Reference: Huang,H., Belwal, T., Li, L., Xu, Y., Zou, L., Lin, X., & Luo, Z. (2021).Amphiphilic and Biocompatible DNA Origami‐Based Emulsion Formation and NanoporeRelease for Anti‐Melanogenesis Therapy. Small, 2104831.
Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.202104831